Lower Back
Want a Stronger, Happier Back? Start Walking
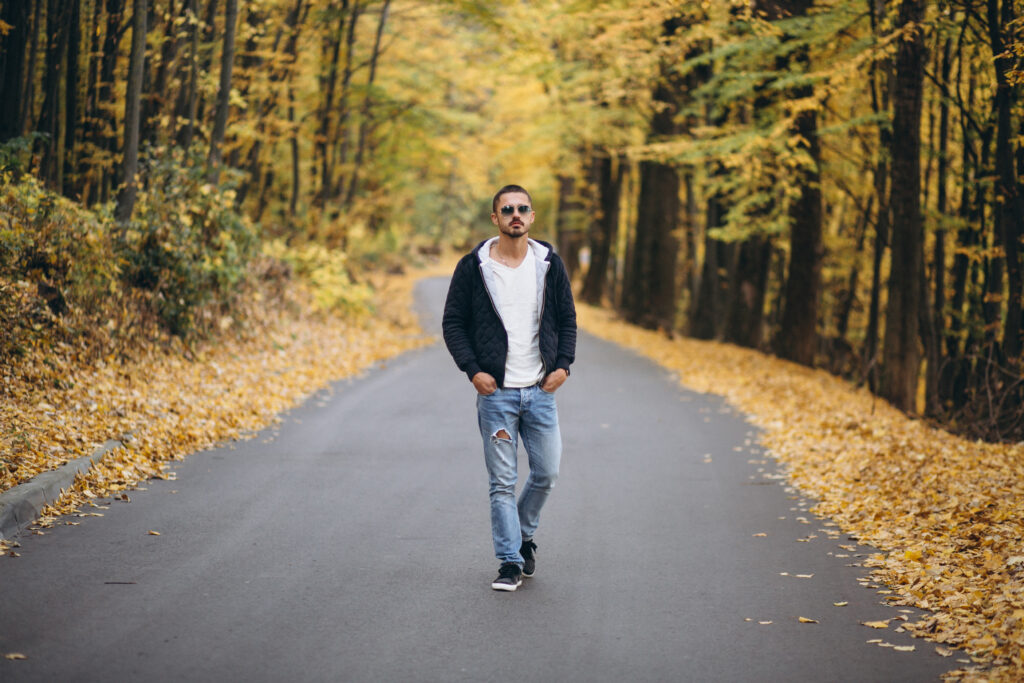

If you’re dealing with nagging back pain, or hoping to avoid it, one of the best things you can do might be the simplest: walk more.
A new study published in JAMA Network Open found that people who walked longer each day were less likely to develop chronic low back pain over time. The findings add to a growing body of research showing that consistent movement is key to keeping your spine healthy and pain-free.
What the Research Found
Researchers followed over 11,000 adults in Norway who didn’t have chronic back pain at the start of the study. Each participant wore an activity tracker to measure how much they walked and how intensely.
About four years later, researchers checked back in to see who had developed chronic low back pain — and a clear trend appeared:
- People who walked around 100 minutes per day had about a 23% lower risk of developing chronic back pain compared to those walking less than 78 minutes daily.
- Walking at a brisk pace helped too, but total walking time mattered more than intensity.
So, it’s not about going faster, it’s about moving more often.
Why Walking Helps Your Back
Walking keeps your spine gently moving, encourages better posture, and strengthens the muscles that support your lower back and hips. It also improves blood flow, reduces stiffness, and releases endorphins that can naturally lower pain levels.
Plus, regular walking helps maintain a healthy body weight, decreases inflammation, and boosts overall mood, all of which contribute to a healthier spine.
How to Get Started
You don’t need fancy equipment or long workouts, just a plan to stay consistent.
Here are a few ways to fit more walking into your day:
- Start with 10–15 minutes after breakfast or lunch.
- Take short breaks from sitting every hour.
- Gradually build up to about 100 minutes per day (roughly 7,000–8,000 steps).
- Mix in core and hip strengthening exercises to support your walking routine.
The key is consistency, small, regular bouts of movement are far better than occasional long walks.
A Note of Realism
This study was observational, meaning it showed a strong link but can’t prove that walking causes less back pain. Still, the evidence supports what most physiotherapists see every day: staying active helps protect your back.
The Bottom Line
Walking is one of the simplest, most effective ways to keep your back strong, flexible, and resilient. It’s free, low-impact, and accessible for nearly everyone — and it may be the best preventive “medicine” your spine could ask for.
If you’re currently managing back pain or unsure how much activity is safe for you, our physiotherapy team can help design a personalized walking and strengthening program to get you moving comfortably again.
Reference
Stensvold D, Steene-Johannessen J, Mikalsen E, et al. Volume and Intensity of Walking and Risk of Chronic Low Back Pain. JAMA Network Open. 2025;8(10):e2333313. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.33313
Low Back Pain

Overview
Low back pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints, affecting people of all ages. It can range from a mild, dull ache to severe, disabling pain. Low back pain can be acute, lasting a few days to weeks, or chronic, persisting for three months or more. Causes vary widely, from muscle strains and poor posture to herniated discs and degenerative diseases.
Symptoms
- Persistent ache or stiffness in the lower back
- Sharp, localized pain in the lower back, particularly after lifting heavy objects or twisting
- Pain that radiates from the lower back to the buttocks, legs, or feet (sciatica)
- Difficulty standing up straight or moving the lower back
- Decreased range of motion in the lower back
- Muscle spasms in the lower back
Causes
- Muscle or Ligament Strain: Often due to heavy lifting, sudden movements, or poor posture.
- Herniated or Bulging Discs: Discs that have slipped or ruptured can press on nerves, causing pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: The wear and tear on spinal discs can lead to chronic pain.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis in the lower back can lead to narrowing of the space around the spinal cord, causing pain.
- Sciatica: Compression of the sciatic nerve can lead to pain radiating from the lower back down the leg.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or improper ergonomics can contribute to chronic low back pain.
- Injuries: Sports injuries, car accidents, or falls can result in low back pain.
Medical Treatments
Initial Care
- Rest: Short periods of rest can help reduce acute low back pain, but extended bed rest is not recommended.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice or heat can reduce pain and inflammation in the lower back.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, can relieve pain and inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: Prescribed to relieve muscle spasms in the lower back.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe pain, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and provide relief.
Specialized Care
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and posture, and to alleviate pain.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments can be used to relieve low back pain, but should be performed by a licensed professional.
- Massage Therapy: Can help relieve muscle tension and improve circulation in the affected area.
- Acupuncture: These treatments can help relieve pain and improve muscle function in chronic cases.
- Surgery: Considered only in severe cases where conservative treatments have failed, particularly for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Role of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing low back pain, focusing on restoring function, relieving pain, and preventing future occurrences.
- Strengthening Exercises: Building core strength to support the spine and reduce the risk of future injuries.
- Stretching Exercises: Enhancing flexibility in the lower back, hamstrings, and hips to reduce tension and pain.
- Postural Training: Educating patients on proper posture and ergonomics to reduce strain on the lower back.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as spinal mobilization and soft tissue massage to improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Activity Modification: Advice on modifying daily activities to avoid aggravating the lower back and to promote healing.
- Education: Providing information on the anatomy of the lower back, safe lifting techniques, and strategies to prevent future back pain.
- Acupuncture and Dry Needling: Used to relieve muscle tension and promote healing in chronic low back pain cases.
- Shockwave Therapy: Utilized in some cases to stimulate tissue repair and manage chronic pain.
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy can help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and accelerate the healing process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes low back pain?
Low back pain can be caused by muscle or ligament strain, herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, arthritis, sciatica, poor posture, or injuries.
How can I prevent low back pain?
Maintaining good posture, staying active, exercising regularly to strengthen the core, and using proper lifting techniques can help prevent low back pain.
When should I see a doctor for low back pain?
You should see a doctor if your low back pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by symptoms like numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs.
What is sciatica and how is it related to low back pain?
Sciatica is a condition where the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the legs, is compressed or irritated. This can cause pain that radiates from the lower back into the buttocks, legs, or feet. Sciatica is often caused by a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or other issues that put pressure on the nerve.
How can I differentiate between general low back pain and sciatica?
General low back pain is usually localized to the lower back and may not radiate beyond this area. In contrast, sciatica typically involves pain that radiates from the lower back down the buttocks, leg, or foot, and is often accompanied by symptoms like numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected leg.
Is physiotherapy effective for low back pain?
Yes, physiotherapy is highly effective in treating low back pain by improving strength, flexibility, and posture, and by providing pain relief.
Can stress contribute to low back pain?
Yes, stress can lead to muscle tension in the lower back, contributing to pain.
How long does it take to recover from low back pain?
Recovery time varies depending on the cause and severity of the pain, but most cases improve within a few weeks with appropriate treatment.
Is surgery necessary for low back pain?
Surgery is rarely needed and is usually only considered in severe cases where there is a structural problem, such as a herniated disc compressing a nerve.
How can I manage low back pain at home?
You can manage mild low back pain at home with rest, ice or heat therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers, and gentle stretching exercises. Avoid activities that strain the lower back.
References
1. Zaina, F., Cote, P., Cancelliere, C., Di Felice, F., Donzelli, S., Rauch, A., … & Nordin, M. (2023). A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines for persons with non-specific low back pain with and without radiculopathy: identification of best evidence for rehabilitation to develop the WHO’s package of interventions for rehabilitation. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation, 104(11), 1913-1927.
2. Nicol, V., Verdaguer, C., Daste, C., Bisseriex, H., Lapeyre, É., Lefèvre-Colau, M. M., … & Nguyen, C. (2023). Chronic low back pain: a narrative review of recent international guidelines for diagnosis and conservative treatment. Journal of clinical medicine, 12(4), 1685.
3. Kholoosy, L., Elyaspour, D., Akhgari, M. R., Razzaghi, Z., Khodamardi, Z., & Bayat, M. (2020). Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of low level laser in controlling low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of lasers in medical sciences, 11(2), 120.
4. Abdelbasset, W. K., Nambi, G., Alsubaie, S. F., Abodonya, A. M., Saleh, A. K., Ataalla, N. N., … & Moawd, S. A. (2020). A Randomized Comparative Study between High‐Intensity and Low‐Level Laser Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain. Evidence‐Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2020(1), 1350281.
5. Li, Y. X., Yuan, S. E., Jiang, J. Q., Li, H., & Wang, Y. J. (2020). Systematic review and meta-analysis of effects of acupuncture on pain and function in non-specific low back pain. Acupuncture in Medicine, 38(4), 235-243.
6. Liu, K., Zhang, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, H., Xu, X., Yuan, Z., & Dong, J. (2023). Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 632 patients. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 18(1), 455.